本文出自明月工作室:https://www.freebytes.net/it/java/shiro-study-3.html
首先,有必要回顾下重要的概念——
subject 相当于用户主体
principals 相当于用户名
credentials 相当于用户密码
realms 相当于访问数据库用户身份数据的DAO,在这里可进行用户信息校验
来看shiro的登录操作——
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("admin", "admin");
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
subject.login(token);可见,subject执行了登录操作,但是它并不直接处理,而是交由securityManager去控制,securityManager也不直接执行,而是又交给了Authenticator去执行。也就是说, Authenticator才是真正的身份认证处理器。
ModularRealmAuthenticator是Authenticator的默认实现类,它的作用是把所有的realm搜集起来,用每一个realm去校验身份信息,然后根据每个realm返回的结果来决定身份认证是否成功。
这几个实体之间的关系,可用下图来表示:
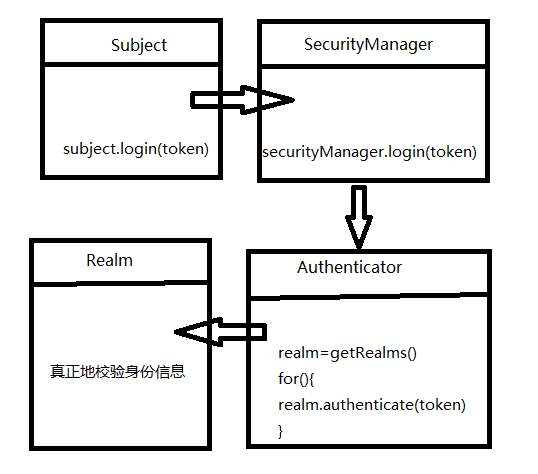
明白大概关系之后,我们直接深入源码作进一步的理解吧:
1、由subject.login(token)方法进入DelegatingSubject类:
public void login(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
clearRunAsIdentitiesInternal();
Subject subject = securityManager.login(this, token);
PrincipalCollection principals;
String host = null;
if (subject instanceof DelegatingSubject) {
DelegatingSubject delegating = (DelegatingSubject) subject;
//we have to do this in case there are assumed identities - we don't want to lose the 'real' principals:
principals = delegating.principals;
host = delegating.host;
} else {
principals = subject.getPrincipals();
}
if (principals == null || principals.isEmpty()) {
String msg = "Principals returned from securityManager.login( token ) returned a null or " +
"empty value. This value must be non null and populated with one or more elements.";
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
this.principals = principals;
this.authenticated = true;
if (token instanceof HostAuthenticationToken) {
host = ((HostAuthenticationToken) token).getHost();
}
if (host != null) {
this.host = host;
}
Session session = subject.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
this.session = decorate(session);
} else {
this.session = null;
}
}从这行代码点进去:Subject subject = securityManager.login(this, token);
进入到DefaultSecurityManager的login方法,这个类是SecurityManager的实现类。(token是指封装了用户在登录页面提交的用户名密码等信息的对象)
public Subject login(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
AuthenticationInfo info;
try {
info = authenticate(token);
} catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
try {
onFailedLogin(token, ae, subject);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("onFailedLogin method threw an " +
"exception. Logging and propagating original AuthenticationException.", e);
}
}
throw ae; //propagate
}
Subject loggedIn = createSubject(token, info, subject);
onSuccessfulLogin(token, info, loggedIn);
return loggedIn;
}其中,info = authenticate(token),调用的就是Authenticator的认证方法:
public AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken)
throws AuthenticationException;然后,一路追踪,经过了抽象子类AbstractAuthenticator,再到达具体的实现子类ModularRealmAuthenticator,它的doAuthenticate()方法就有调用realm的逻辑:
protected AuthenticationInfo doAuthenticate(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
assertRealmsConfigured();
Collection<Realm> realms = getRealms();
if (realms.size() == 1) {
return doSingleRealmAuthentication(realms.iterator().next(), authenticationToken);
} else {
return doMultiRealmAuthentication(realms, authenticationToken);
}
}一般只需要一个realm,所以会执行doSingleRealmAuthentication()方法,如果有多个,会执行doMultiRealmAuthentication()。
protected AuthenticationInfo doSingleRealmAuthentication(Realm realm, AuthenticationToken token) {
if (!realm.supports(token)) {
String msg = "Realm [" + realm + "] does not support authentication token [" + token + "]. Please ensure that the appropriate Realm implementation is " + "configured correctly or that the realm accepts AuthenticationTokens of this type.";
throw new UnsupportedTokenException(msg);
}
AuthenticationInfo info = realm.getAuthenticationInfo(token);
if (info == null) {
String msg = "Realm [" + realm + "] was unable to find account data for the " + "submitted AuthenticationToken [" + token + "].";
throw new UnknownAccountException(msg);
}
return info;
}这句代码realm.getAuthenticationInfo(token),真正进入了Realm的api。
AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException;Realm是一个接口,getAuthenticationInfo这个方法具体的实现在它的抽象子类AuthenticatingRealm。 这一个方法对于理解源码来说,至关重要。 (以下代码有注释,请细看)
public final AuthenticationInfo getAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
//如果有缓存,从缓存中获取认证信息
AuthenticationInfo info = getCachedAuthenticationInfo(token);
if (info == null) {
//没有缓存,就执行以下代码
//doGetAuthenticationInfo这是个抽象方法,表示需要由子类去实现,也
//就是我们自定义的realm需要重写的方法。
info = doGetAuthenticationInfo(token);
log.debug("Looked up AuthenticationInfo [{}] from doGetAuthenticationInfo", info);
if (token != null && info != null) {
cacheAuthenticationInfoIfPossible(token, info);
}
} else {
log.debug("Using cached authentication info [{}] to perform credentials matching.", info);
}
if (info != null) {
//执行密码匹配校验逻辑
assertCredentialsMatch(token, info);
} else {
log.debug("No AuthenticationInfo found for submitted AuthenticationToken [{}]. Returning null.", token);
}
return info;
}
protected abstract AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException;AuthenticatingRealm是个抽象类,我们平时自定义的Realm都是直接或者间接地继承于它。
doGetAuthenticationInfo()是需要我们自定义的Realm去重写的,需要返回一个表示身份信息的对象AuthenticationInfo ,这跟AuthenticationToken 不一样,后者是用户在登录窗口提交的信息,不一定是准确的;前者确是根据用户提交的用户名,从数据库中,查询出来的带有该用户真正的密码等信息的对象。
然后shiro使用这个真正的身份信息对象,与登录窗口提交的身份信息对象,传入assertCredentialsMatch()方法,进行密码比对。如果密码比对正确,才能最终完成认证。
protected void assertCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationInfo info) throws AuthenticationException {
CredentialsMatcher cm = getCredentialsMatcher();
if (cm != null) {
if (!cm.doCredentialsMatch(token, info)) {
//not successful - throw an exception to indicate this:
String msg = "Submitted credentials for token [" + token + "] did not match the expected credentials.";
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException(msg);
}
} else {
throw new AuthenticationException("A CredentialsMatcher must be configured in order to verify " +
"credentials during authentication. If you do not wish for credentials to be examined, you " +
"can configure an " + AllowAllCredentialsMatcher.class.getName() + " instance.");
}
}这里又引出了一个CredentialsMatcher的概念,其实也就是密码校验器。之所以没有直接在realm里面写密码校验的逻辑,是为了解耦,为了方便用户自定义密码校验规则。如用户想要自定义密码校验器,只需要这样:
//这段代码是基于Spring的环境写的,如果没有spring,那么需要将一下代码转化
//为ini的配置文件代码
AuthenticatingRealm customRealm = new CustomRealm();
customRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(new CredentialsMatcher() {
@Override
public boolean doCredentialsMatch(AuthenticationToken token,
AuthenticationInfo info) {
return true;
}
});shiro提供的默认密码校验器 SimpleCredentialsMatcher 比较简单,它的实现是,直接将用户提交的AuthenticationToken数据与数据库中的数据进行简单的等值比较。这肯定是不满足于企业级项目的需要的。
但是它提供了一个 HashedCredentialsMatcher,它支持先将密码进行hash计算,再与数据库中的值进行比对的操作,同时支持加密和加盐的操作。如果需要使用它,那么在创建用户时就应该对密码进行加盐、加密计算(你只加密不加盐也可以,但最好还是两者皆用):
RandomNumberGenerator rng = new SecureRandomNumberGenerator();
Object salt = rng.nextBytes();
String hashedPasswordBase64 = new Sha256Hash(plainTextPassword, salt, 1024).toBase64();
User user = new User(username, hashedPasswordBase64);
//将盐值保存到数据库
user.setPasswordSalt(salt);
userDAO.create(user);然后,配置验证时用的Realm和密码校验器——
//这段代码是基于Spring的环境写的,如果没有spring,那么需要将一下代码转化
//为ini的配置文件代码
AuthenticatingRealm customRealm = new CustomRealm();
HashedCredentialsMatcher credentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
credentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
credentialsMatcher.setStoredCredentialsHexEncoded(false);
customRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(credentialsMatcher);最后,还得在doGetAuthenticationInfo()方法中返回一个SaltedAuthenticationInfo对象,替代普通的AuthenticationInfo对象,这个对象会把salt值带过去,给到校验器工作。
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
// 获取用户名
UsernamePasswordToken token = (UsernamePasswordToken) authenticationToken;
String username = token.getUsername();
User user = null;
try {
user = userService.getUserByName(username);
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) {
throw new IncorrectCredentialsException(e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (LockedAccountException e) {
throw new LockedAccountException(e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (ExcessiveAttemptsException e) {
throw new ExcessiveAttemptsException(e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("对用户[" + username + "]进行登录验证..验证未通过{}", e.getMessage());
throw new AuthenticationException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
//进行验证
SaltedAuthenticationInfo authenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(
user, //用户
user.getPassword(), //密码
ByteSource.Util.bytes(user.getSalt()), //设置盐值
getName()
);
return authenticationInfo;
}

终于明了了,感谢大佬!