本文出自明月工作室:https://www.freebytes.net/it/java/springboot-zujian.html
maven仓库上大部分的jar包都是不包括web功能的,比如junit、spring-core、hibernate等,但是spring-boot-starter-web是具有web功能的,可以凭此开发web网站。 spring-boot-starter-web 也是一个开发springboot项目所必备的依赖jar包,这种被应用项目所依赖引用的jar包也叫做组件。那么一个springboot项目其本身是否也能作为一个组件被另一个springboot项目依赖引用呢?
简单地说,其实就三步,删除springboot项目的启动类,删除pom中的 springboot专用打包插件 spring-boot-maven-plugin,然后就可以用mvn install或者mvn deploy将其发布到本地或者远程,它就是个组件了。如果没有耐心看下文,看到这里诸位就可以去试试了。
但是其中的细节和优化,还是需要通过示例项目来详细说明。
两个示例项目
我们来建立两个maven项目,分别是net.freebytes.test1,net.freebytes.test2
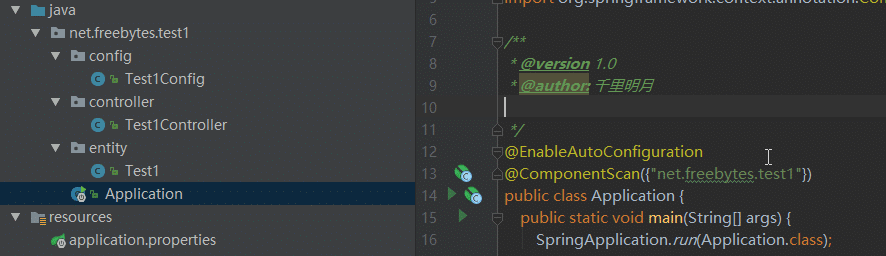
启动类Application.java
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class);
}
}实体类Test1.java
public class Test1 {
private String name="test1";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}配置类Test1Config .java
@Configuration
public class Test1Config {
@Bean
public Test1 test1() {
return new Test1();
}
}controller类Test1Controller.java
@RestController
public class Test1Controller {
@Autowired
private Test1 test1;
@RequestMapping("/test1")
public void test1() {
System.out.println(test1.getName());
}
}pom文件
<groupId>net.freebytes</groupId>
<artifactId>test1</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>配置文件application.properties
server.port=8080
test2项目代码基本跟test1的一致,只是类名和端口不一样。
分别跑起项目,测试 http://localhost:8080/test1 和 http://localhost:8081/test2 ,运行无碍即可。
组件改装
接下来,我们把test2项目改装成组件,并在test1项目中引入test2组件。
第一步,删除启动类,并注释掉pom中的springboot打包插件spring-boot-maven-plugin,项目最终如下——

此时运行mvn clean package install ,将组件发布到本地仓库,它的组件id就是
<groupId>net.freebytes</groupId>
<artifactId>test2</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>第二步,test1中引入组件,即是在test1的pom文件中引入test2的组件id,这样test1的中依赖就变成了两个——
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.freebytes</groupId>
<artifactId>test2</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>第三步,在test1的启动类中拓展扫描范围,确保能够扫描到test2的包——
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan({"net.freebytes.test1","net.freebytes.test2"})
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class);
}
}这样子其实,就成功了,点击启动类运行即可,在浏览器输入 http://localhost:8080/test1 和 http://localhost:8080/test2 ,都可以正常访问。可能有人会担心test2的application.properties配置文件还未删除,会不会影响到test1本身的配置,其实不会,springboot不会去读取那个配置文件的。另外,由于已经引入了test2,因此test2中已注册到spring容器的bean都可以直接在test1中装配,如——
@RestController
public class Test1Controller {
@Autowired
private Test1 test1;
@Autowired
private Test2 test2;
@RequestMapping("/test1")
public void test1() {
System.out.println(test1.getName());
System.out.println(test2.getName());
}
}组件改装优化
但是,企业级的组件其实一般都不会将所有的bean都配置好,而是将一部分必须的bean配置好,暴露非必须的bean由用户自由配置,例如这里的test2项目中的Test2Config.java——
@Configuration
public class Test2Config {
@Bean
public Test2 test2() {
return new Test2();
}
}这里声明了@Configuration并在方法中声明了@Bean,也就是把test2对象配置好了,如果开发test1项目的用户其实并不需要这个test2对象,那么这个对象就白配了,也浪费了内存。优化方式有三种——
方式一:将Test2Config.java 改成这样
public class Test2Config {
@Bean
public Test2 test2() {
return new Test2();
}
}这个bean就不会被装配,然后在test1项目中将Test1Config.java改成——
@Configuration
public class Test1Config {
@Bean
public Test1 test1() {
return new Test1();
}
@Bean
public Test2 test2(){
return new Test2();
}
}方式二: 将Test1Config.java 和 Test2Config.java 改成这样
// Test1Config.java -----------------
@Configuration
@Import(Test2Config.class)
public class Test1Config {
@Bean
public Test1 test1() {
return new Test1();
}
}
// Test2Config.java -----------------
public class Test2Config {
@Bean
public Test2 test2() {
return new Test2();
}
}方式三: 将Test1Config.java 和 Test2Config.java 改成这样
// Test1Config.java -----------------
@Configuration
public class Test1Config {
@Bean
public Test1 test1() {
return new Test1();
}
}
// Test2Config.java -----------------
public class Test2Config {
@Bean
public Test2 test2() {
return new Test2();
}
}然后在Test1的resources目录下建立META-INF目录,然后在该目录下新建spring.factories文件,文件中输入——
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=net.freebytes.test2.config.Test2Config

这样,就使得组件中的bean交给了Test1项目去自由装配。
上述三种方式,都是将Test2的bean交由了Test1项目去创建的,所以其启动类都可以改为——
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan({"net.freebytes.test1"})
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class);
}
}
